Aerodynamics » Energy
2.2 Energy
This change in velocity implies a corresponding change in kinetic energy (KE=½ mv2). The principle known as Conservation of Energy suggests that unless extra energy is introduced into a moving airstream (such as fuel) the overall energy content must remain unchanged from one point to another. Hence, if KE increases some other energy form decreases.
Bernoulli's equation highlights the relationship between pressure energy and kinetic energy.
-
P
+
½ ρ V2
=
Constant
Pressure
(static)
Kinetic
(dynamic)
“Pitot”
This can be expressed as P1 + ½ ρ V12 = P2 + ½ ρ V22. This implies that if V2 is greater than V1 (as in the throat of a venturi, then P2 is less than P1, i.e. there is a drop in pressure).This is of particular interest to students of aeronautics because the flow through a venturi has similar characteristics to the flow over an aerofoil. (The aerofoils cambered shaped is virtually the shape of a venturi). Bernoulli's equation showing the relationship between changes of pressure and velocity is used to explain the "lifting" effect of aerofoil (see figure 1.6).
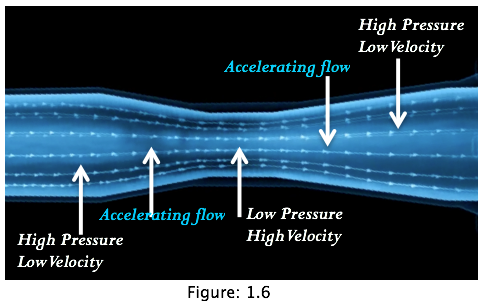
Air accelerates when flowing from high pressure region to low pressure region.
